Every application has its own set of environment variables, and it helps them determine where to install and store files. These variables contain names and values that help control the operational environment. Further, they have a significant effect and enable your computer’s active processes. Without environment variables, you’ll need to inform your scripts every time to find the same path to a specific file. But if you set a dedicated variable, the information becomes available everywhere.
How to Set Windows Environment Variables
In Windows, the environment variables are categorized into two – User and System. While the former deals with user-defined settings (user profiles, files, etc.), the latter contains the values used by the operating system. In this section, you will learn how to set Windows environment variables via the graphical user interface, command line interface (Command Prompt and Windows Powershell), and Registry Editor. So, without further delay, let’s get right into them in detail.
Using Windows GUI
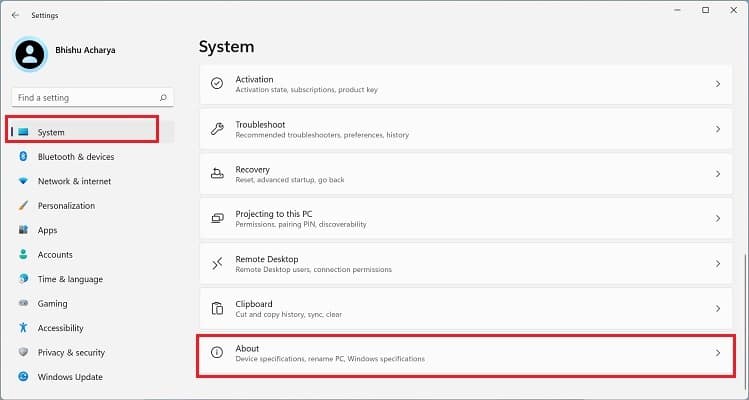
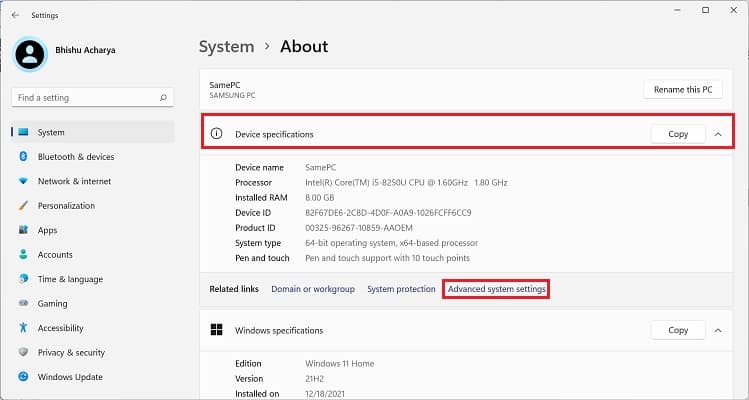
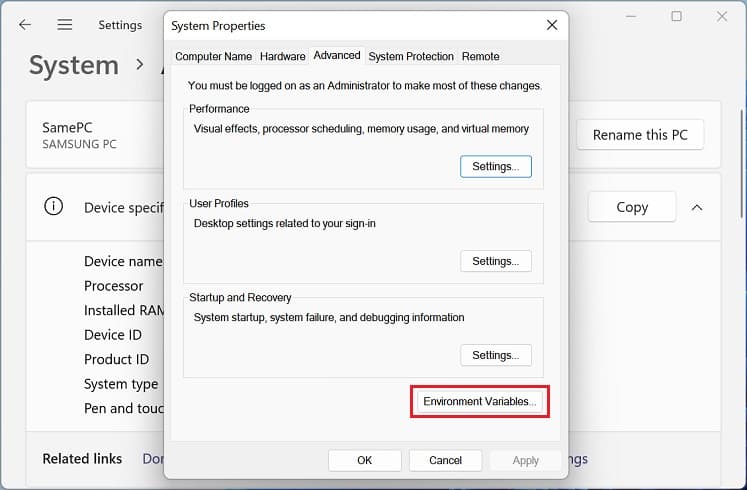
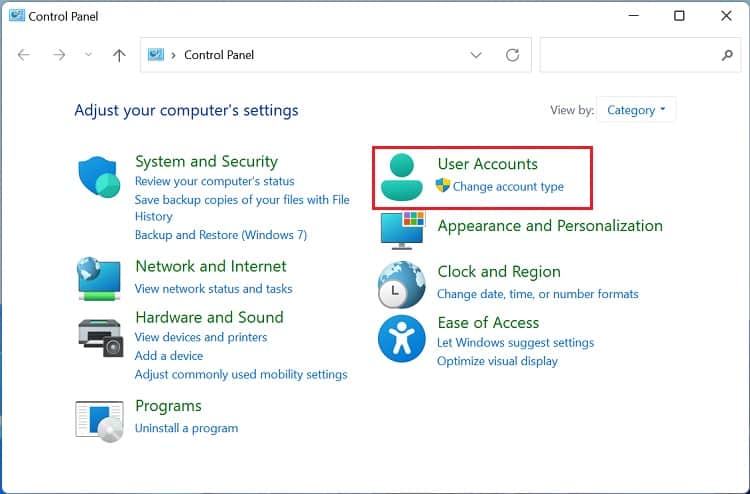
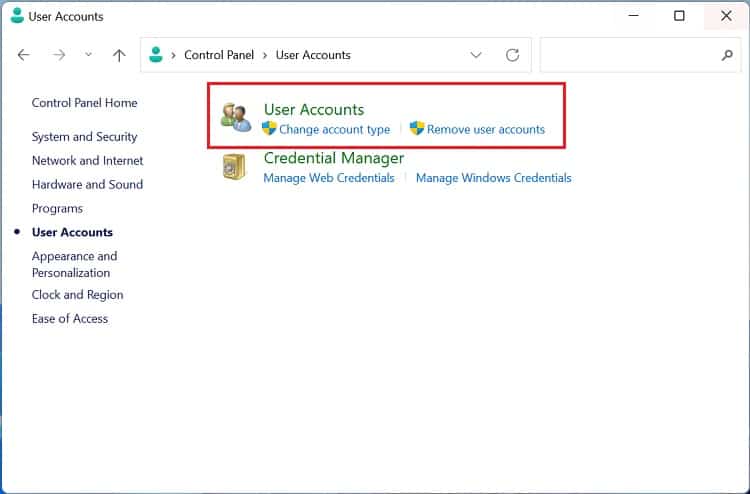
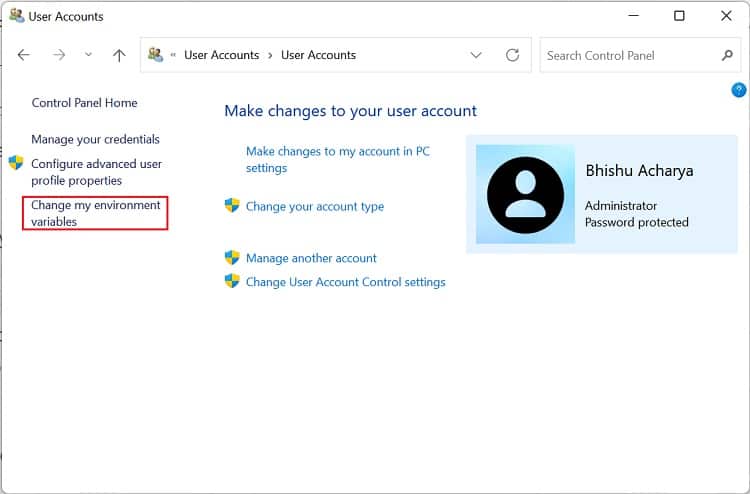
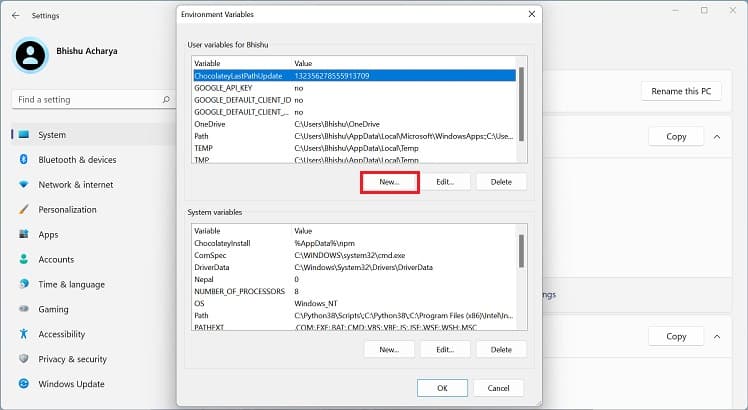
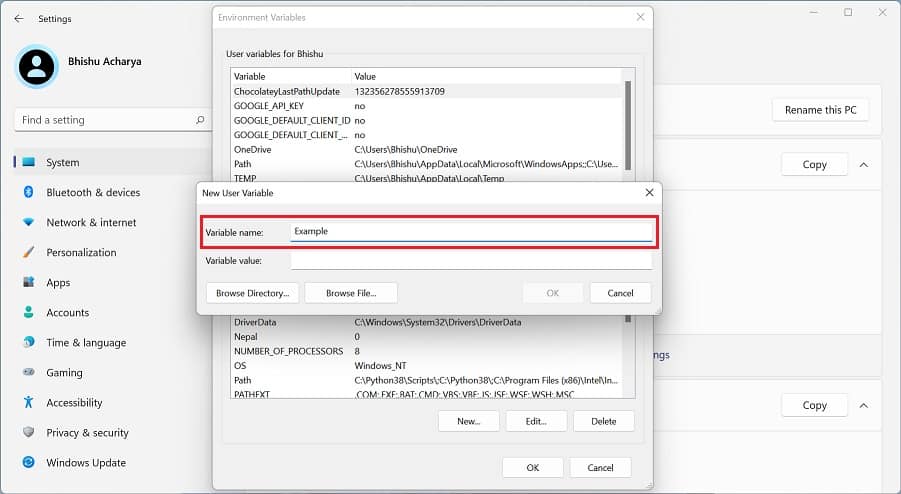
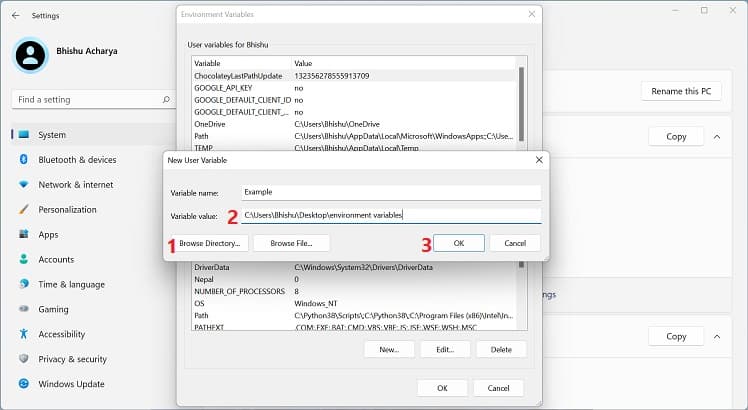
Before setting up a Windows environment variable in the graphical user interface, you’ll need to navigate to the dedicated window: Another way to open Environment Variables window is from the Control Panel utility. Kindly follow the below instructions on how you can do so: Alternatively, you can directly launch it from the Run dialogue box by running the following command:rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariablesAlso, this is possible from the Start menu, where you can search for “Edit the system environment variables” or “Edit environment variables for your account”. Once the Environment Variables window pops up, go through the following guide to learn how to set the system environment variables on Windows 11: You can select the system or user variable if you want to change its name or value. Then, press the Edit button, and proceed with the same steps as above. Likewise, to delete an existing environment variable, select it and choose Delete.
In Registry Editor
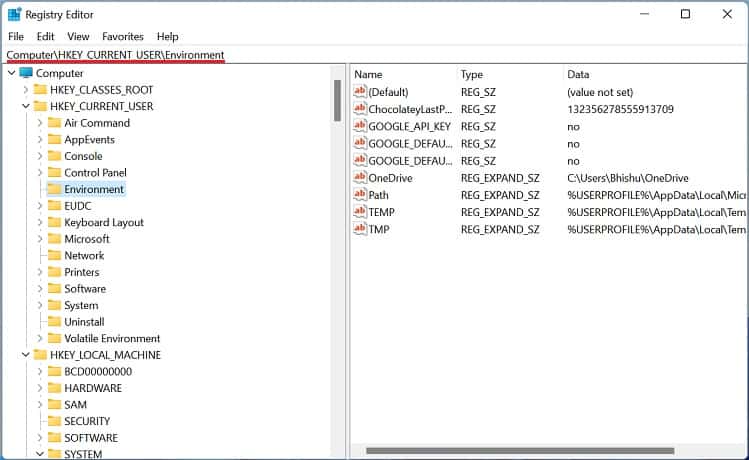
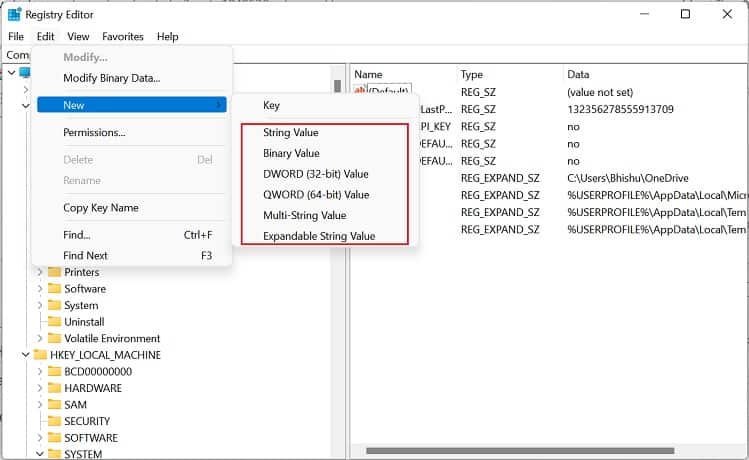
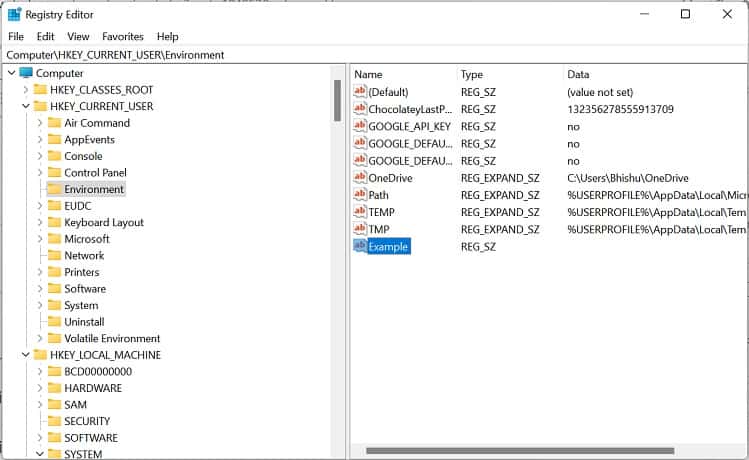
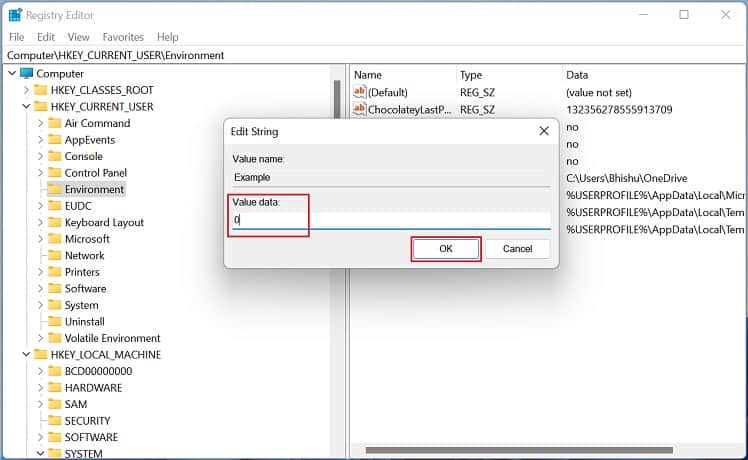
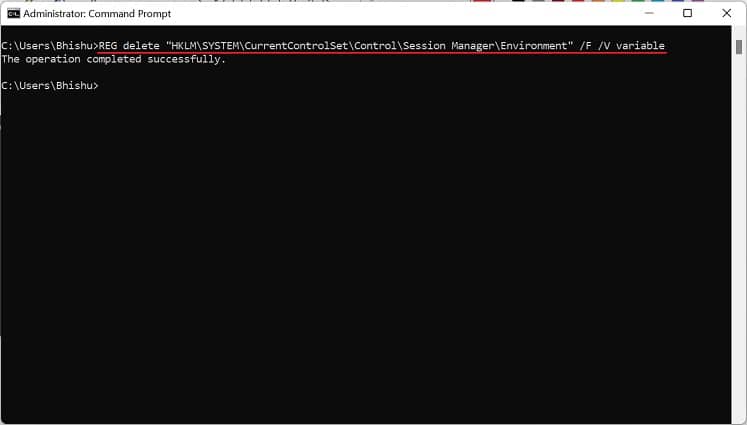
Another way to set Windows environment variables is from the built-in Registry Editor tool. In fact, this is the precise location where all the user and system values are stored. Here’s a quick guide on how to do it the right way: To edit the value, simply double-click the variable and change it to an appropriate one. Furthermore, you can right-click and pick Delete to remove the environment variable permanently.
In Command Prompt
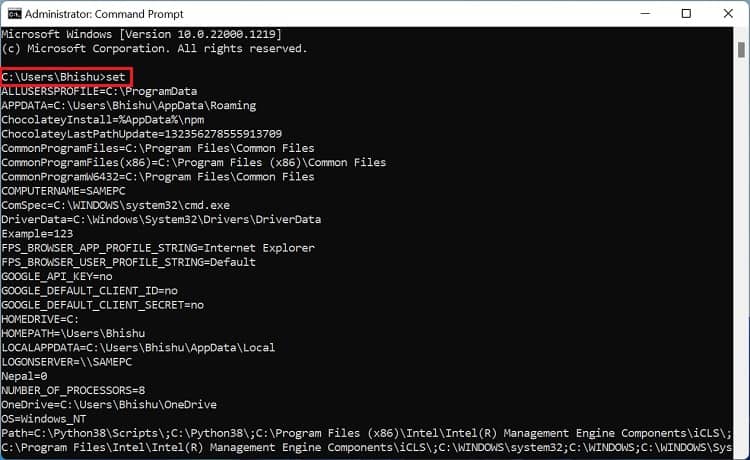
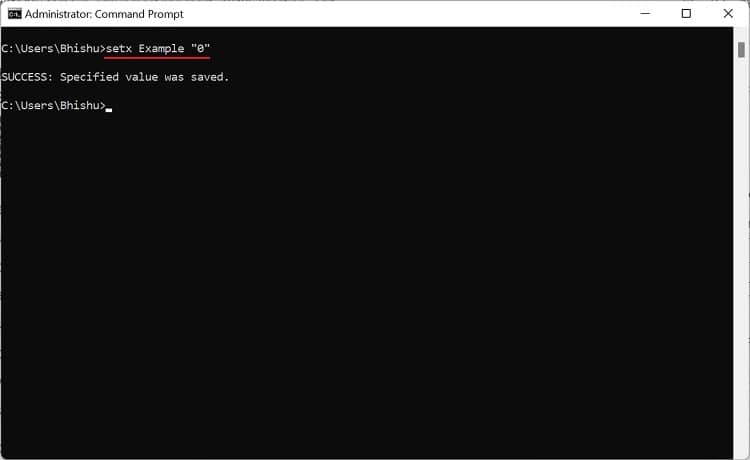
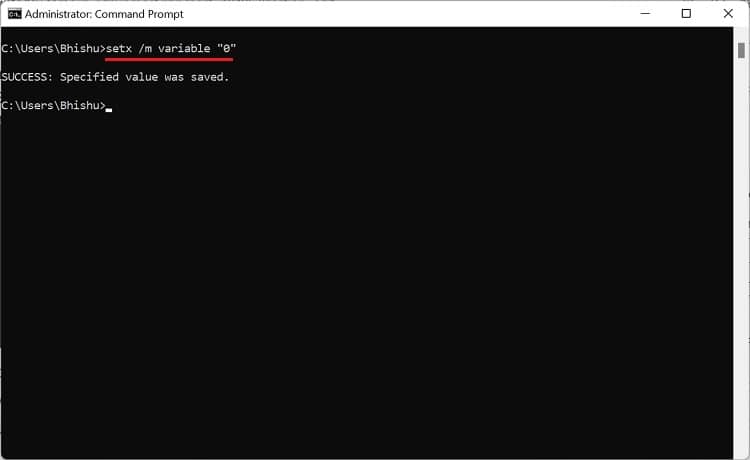
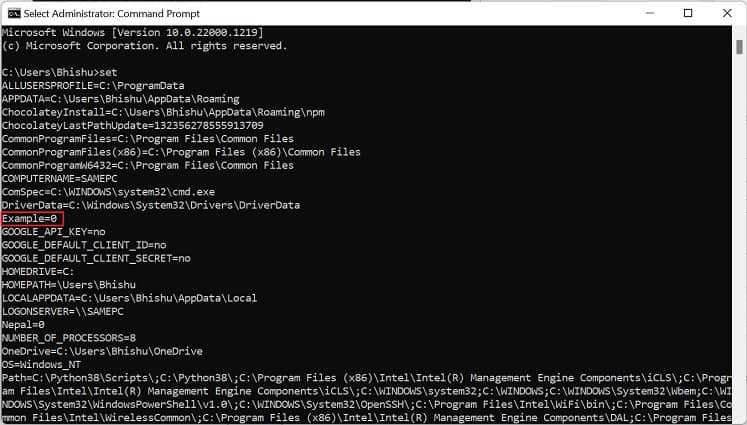
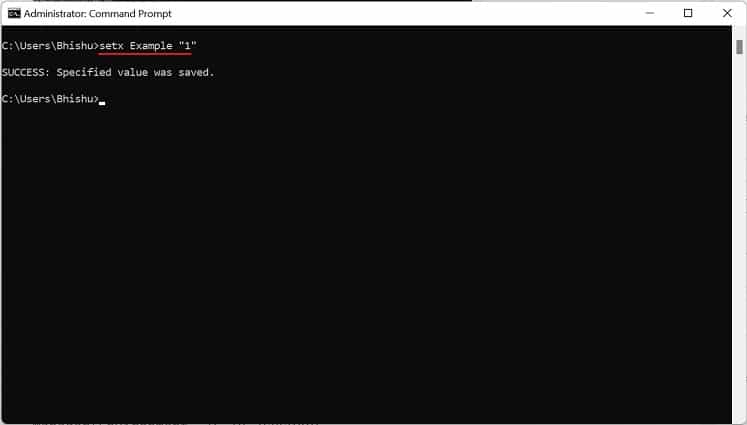
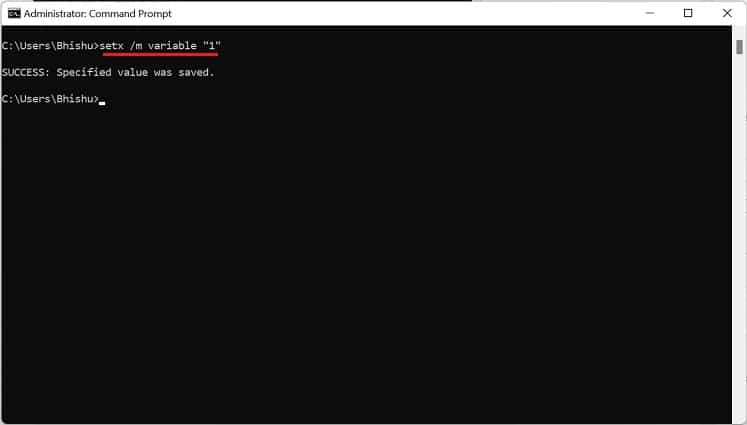
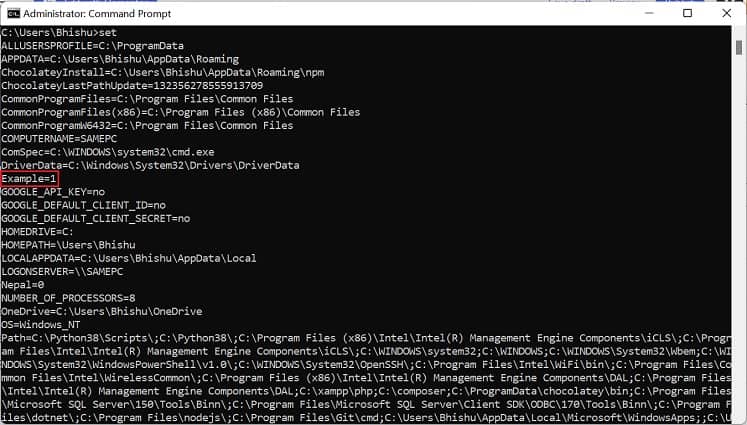
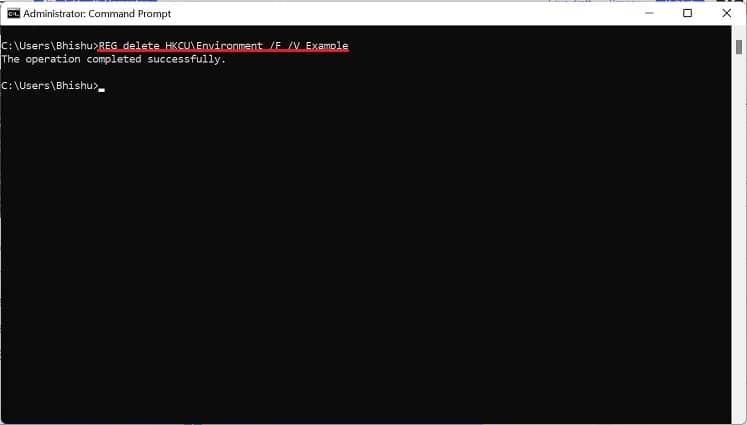
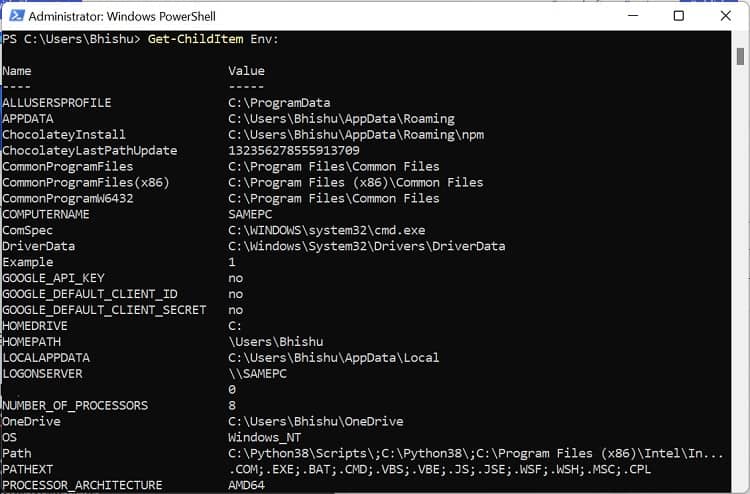
If you prefer CLI (Command Line Interface) over GUI, the good news is that you can use simple commands to set Windows environment variables. Although you can create both user and system variables, there’s no individual section to display each of them. Follow the below steps to view, set, edit, and delete Windows environment variables using Command Prompt:
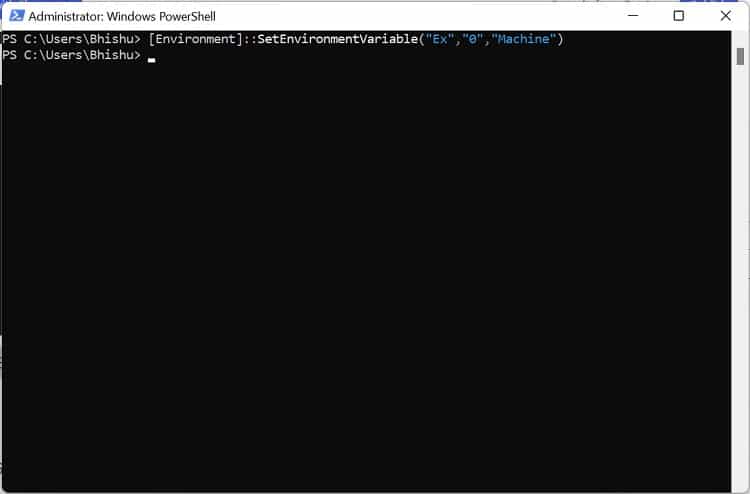
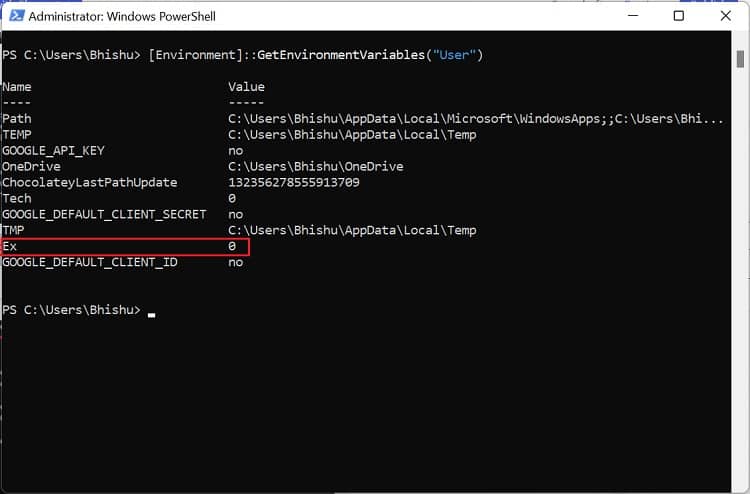
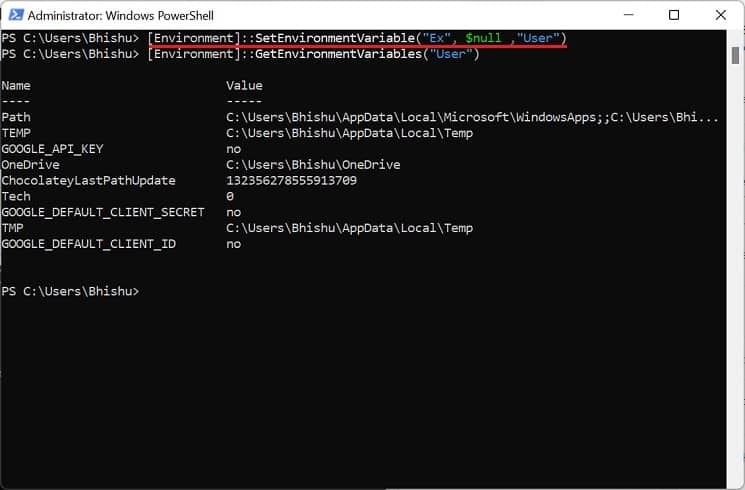
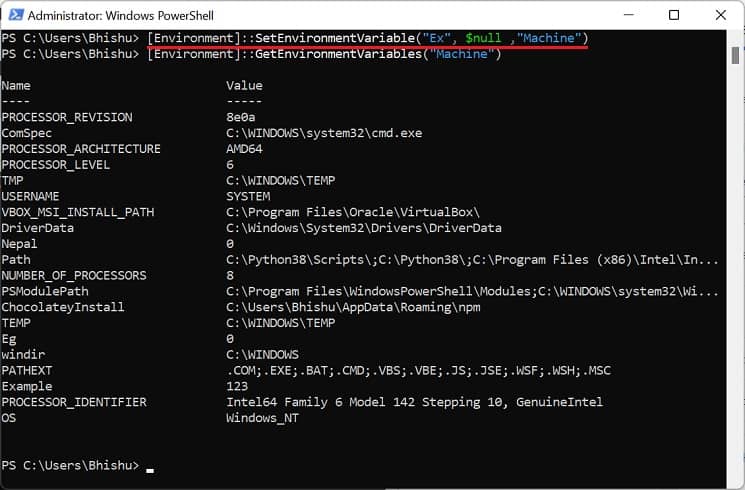
In Windows Powershell
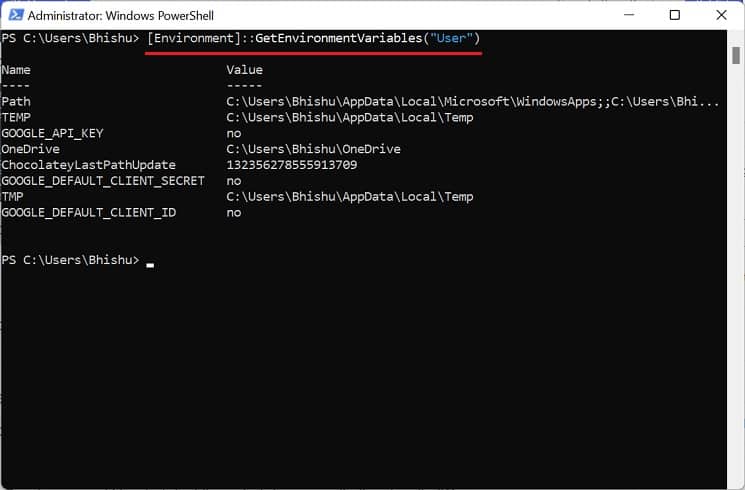
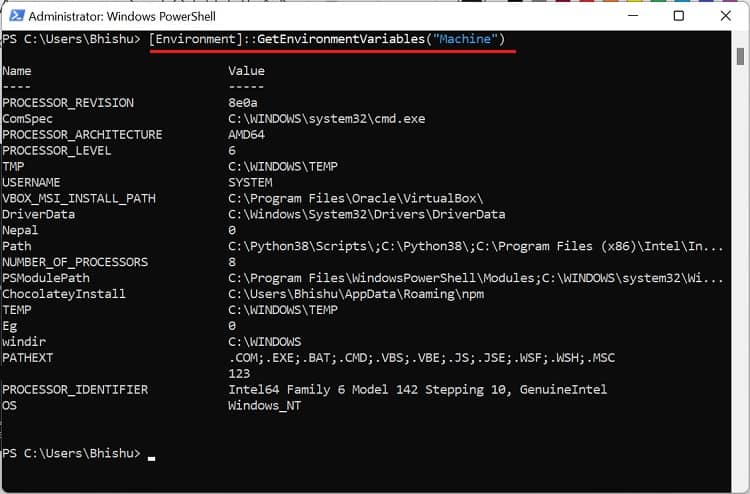
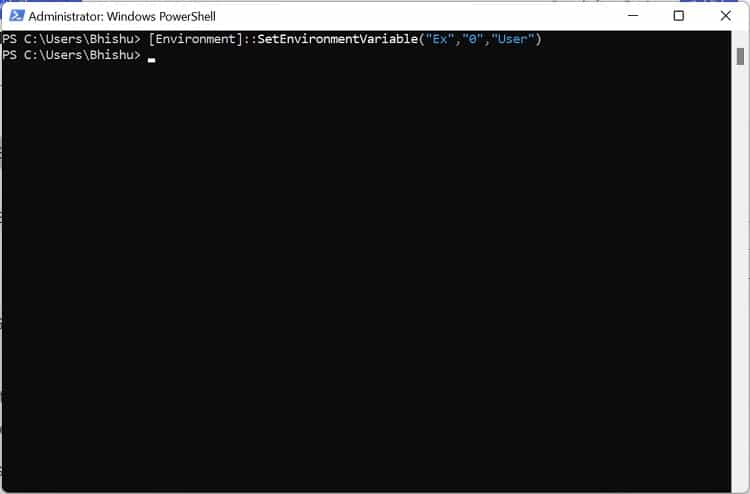
Although Command Prompt is quite popular, most advanced Windows users prefer Powershell due to its extensibility. If you fall into this category, follow our guide to view, set, edit, and delete Windows environment variables via Powershell: